What is Distributed Access Architecture?
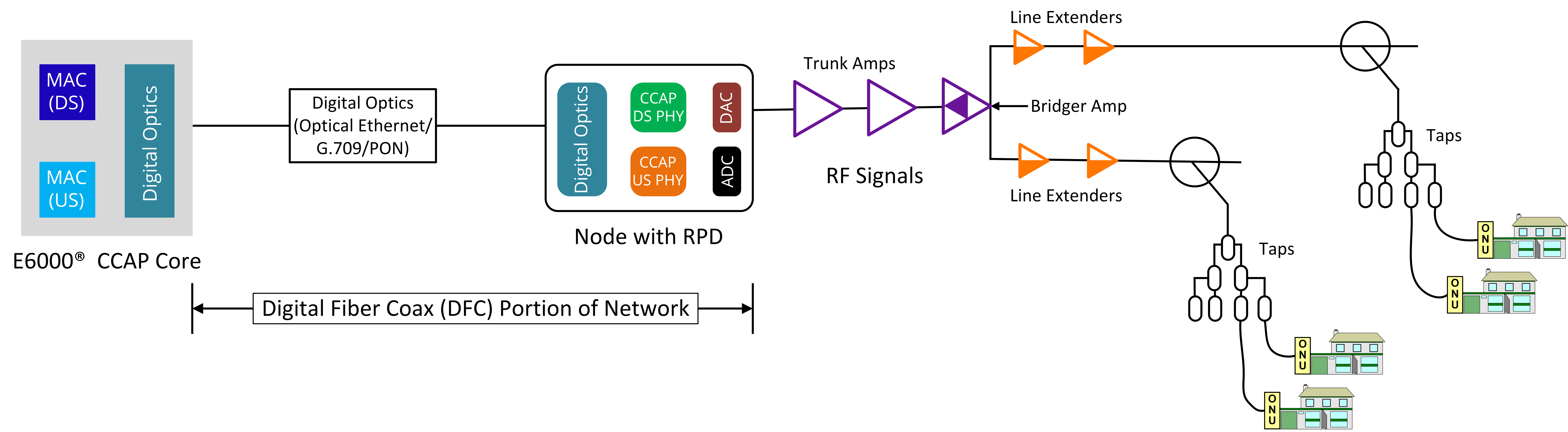
Distributed Access Architecture (DAA) is a network design approach that decentralizes and virtualizes key functions within broadband infrastructure. It enables service providers to improve network efficiency, increase bandwidth capacity, and optimize fiber utilization by shifting processing closer to the network edge.
Key Takeaways
-
Decentralized network design: DAA shifts processing functions closer to the network edge, helping improve efficiency and responsiveness in broadband infrastructure.
-
Digital fiber replaces analog links: By using Ethernet-based digital fiber connections, DAA enhances signal quality, reduces latency, and supports IP-based service delivery.
-
Boosts network performance and capacity: DAA increases bandwidth availability, improves spectral efficiency, and optimizes fiber utilization, making networks more scalable.
-
Operational and maintenance benefits: The architecture simplifies network management, reduces operational costs, and minimizes reliance on legacy analog systems.
-
Supports advanced HFC deployments: DAA enables technologies like Remote PHY and Remote MAC-PHY, allowing service providers to modernize HFC networks while maintaining backward compatibility.
How Distributed Access Architecture Works
DAA replaces traditional analog fiber connections with digital fiber Ethernet links, allowing operators to extend IP-based networks deeper into their service areas. This transition enhances signal quality, reduces latency, and supports next-generation broadband applications.
Advantages of Distributed Access Architecture
DAA offers several benefits, including higher network capacity, simplified maintenance, and reduced operational costs. By eliminating analog fiber dependencies, service providers can improve spectral efficiency, optimize wavelength usage, and enhance overall network performance.
Applications in Broadband Networks
DAA is widely used in Hybrid Fiber-Coaxial (HFC) networks, where it enables the deployment of Remote PHY and Remote MAC-PHY solutions. These technologies help service providers transition to digital fiber while maintaining compatibility with existing infrastructure.